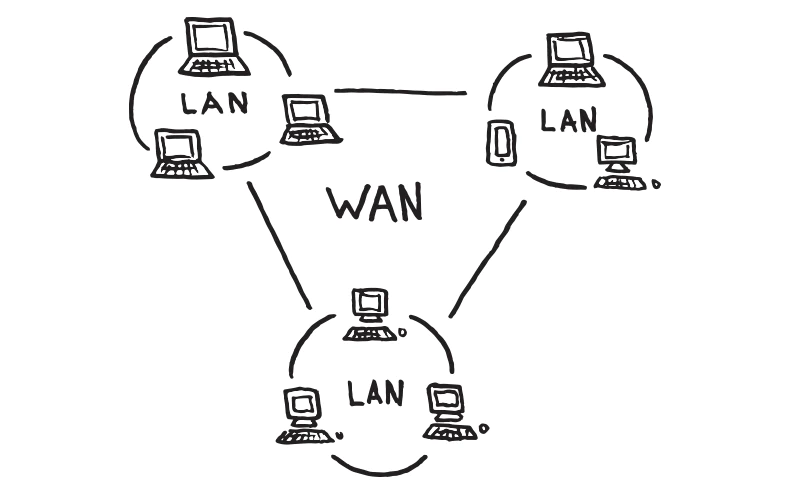
The network of connected devices, workstations, and servers defined for your business is your organization’s backbone. For your operations to run smoothly and securely, your communications network must be optimized for the specific needs of your business.
Today’s two main network options are WAN (Wide Area Network) and LAN (Local Area Network). Let us take a close look at the WAN vs. LAN debate and explore how each of the network features functions and how they differ. These inputs should give you a comparative overview of the network options available before you arrive at decisions about network deployment.
Now let us begin with definitions of both network options before we compare individual features.
What are the Differences Between WAN and LAN?
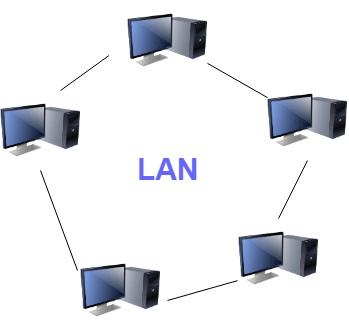
- Defining Local Area network: What is LAN?
A local area network is a group of computers and peripherals connected in a limited area, such as a school, laboratory, home, or office building. The full form of a LAN is a local area network, which is widely helpful for sharing network resources such as files, printers, games, and other applications. The simplest local area network connects computers and printers in someone’s home or office. Generally, the local area network is used as a single transmission medium.
- Defining Wide Area Network:What is WAN?
What is WAN? WAN (Wide Area Network) is a vital computer network spread over a wide geographical area. WAN network systems can be LAN connections that connect to other local area networks using telephone lines and radio waves.
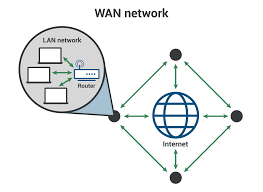
In most cases, it is limited to a company or organization. State-of-the-art communication circuits mostly form a broadband connection.
- Applications
- Local Area Network Application
Here are some typical local area network applications:
- One computer on the network can be configured as a server that can control all the other computers. The LAN allows the software to be stored on a server accessible by all internet users.
- This allows all workstations in the building to be connected so they can communicate locally without an internet connection.
- It helps share resources such as printers and scanners.
- Software developers can also use a LAN to share development/testing tools in an office or factory using the client-server model of a network system.
2. WAN application
Here are some typical WAN applications:
- A department manager in a corporate office wants to share information with his regional office partners, who can then share the information by storing it on a centralized node.
- Military operations require a highly secure communications network. This scenario uses a WAN network.
- Railway reservations and airlines use WANs.
- The dean and university faculty can easily share information or resources because they have a standard network.
- The WAN allows workstations to be connected locally, helping each node communicate with the other without an Internet connection.
- Resources such as printers, scanners, hard drives, and fax machines allow all nodes to be shared publicly.
WAN vs. LAN: What are the differences between WAN and LAN?
Let’s see what are the differences between WAN and LAN. A LAN is a network device group that allows communication between connected devices in a small area. Conversely, a WAN spans a broader scope, such as a country or continent. This network is usually expensive and may not be owned by a single organization.
Below is a list of other differences between WANs and LANs:
- LANs have higher data rates, while WANs have lower data rates.
- LAN offers greater fault tolerance than WAN.
- LAN ownership is private, while WAN ownership can be either public or private.
- The propagation delay in LAN is shorter, while the propagation delay in WAN is longer.
- LAN is less congested than WAN due to space limitations.
- LAN operates on a broadcast basis, while WAN operates on a point-to-point basis.
- The data transmission medium used in a local network is a coaxial or UTP cable. On the other hand, WAN uses PSTN and satellite connections as transmission and communication mediums.
- LANs typically use connection technologies such as tokens and Ethernet. In contrast, WAN uses technologies such as X.25 and trunking to connect longer distances.
- WAN vs. LAN costs – Setting up a WAN to maintain a high network costs more than a LAN. A WAN requires more advanced hardware, such as bridges and workstations, and initial setup costs include firewalls. The cost of setting up a LAN is as low as networks and devices. They can also be maintained at a lower price because they cover a smaller geographic area.
- WAN vs. LAN Ports and Cables – The LAN uses Ethernet cables or wireless cards for connectivity. It starts with a central access point like a router or software. Copper cable is often used when fiber optic networks are available in the home or Wi-Fi to provide wireless networks in a local area network.
- Modern LAN routers usually connect devices wirelessly. However, wired connections such as Ethernet cables are faster because they have less interference.
- WANs are more complex and require a port that connects the router to the outside world. WANs can be connected using wired services such as T1 cables, Direct Internet Access, Metro Ethernet, or wireless services such as cellular networks, satellite signals, and public Wi-Fi.
LAN vs.WAN vs. Ethernet
Ethernet is easily the most common type of LAN. Unlike a WAN, which covers a large geographic area, a local area network is typically connected to computers in a small area. In a world where Wi-Fi is prominent, you may be wondering if your computer has room for an Ethernet port. Well, the answer to that question is yes. And here’s why: Ethernet supports speeds up to 1000 Mbps. In addition, the Ethernet signal is stable, flexible, and secure. Ultimately, your use of Ethernet depends on your preferences, needs, and budget.
How Spectra can Optimize your Business Technology
There are several factors when choosing between WAN vs LAN for your business. However, in most cases, LAN is sufficient for most SMBs because it is easy to install and reduces operational costs. If you need help building and maintaining business networks, Spectra can help. We combine industry expertise with proprietary technology to create comprehensive, secure, intuitive solutions.
